Description
HOW IT WORKS
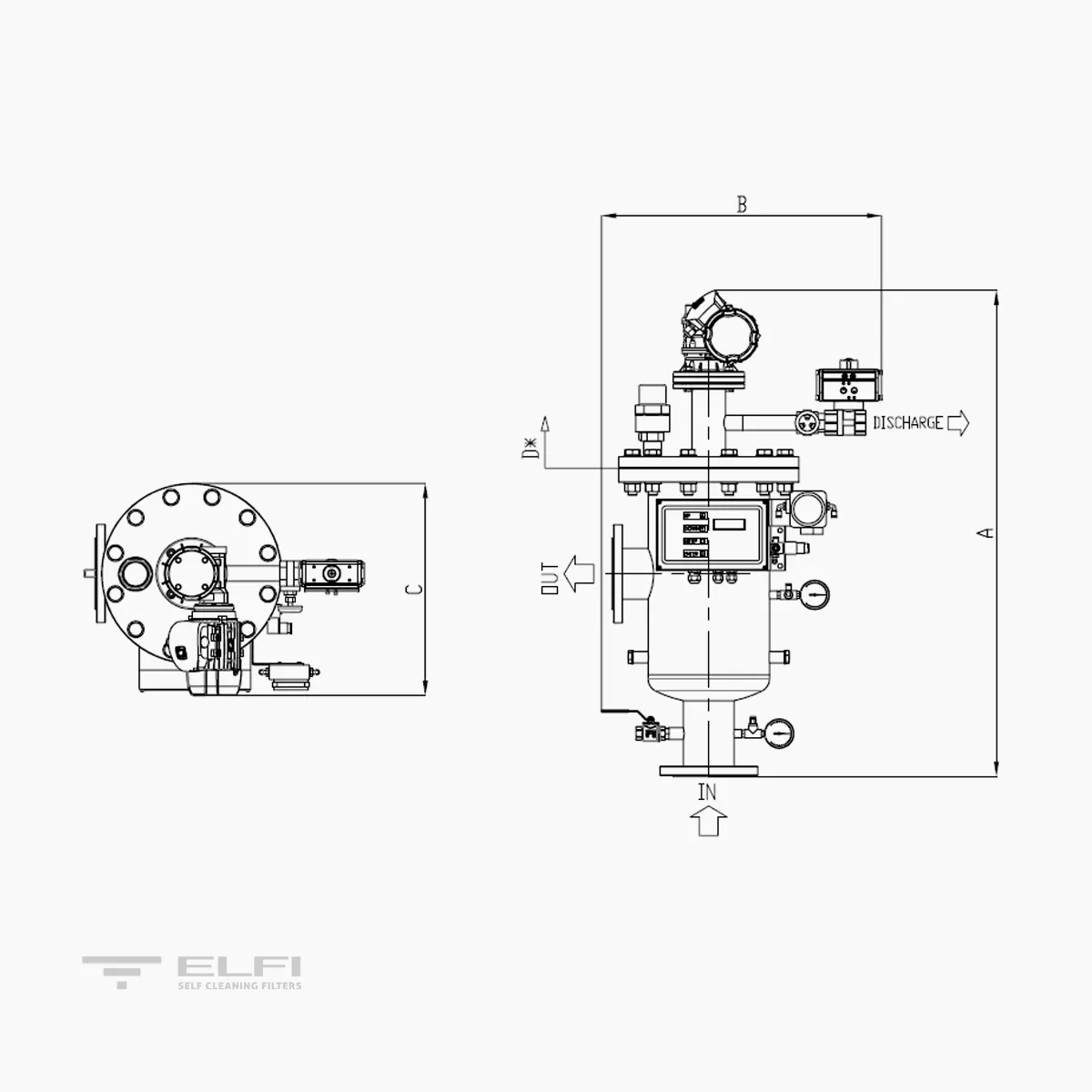
Water enters the filter through the IN inlet and goes through the filtering cylinder from the inside to the outside. This will retain all non-deformable suspended solids that are the same size or bigger than the filtration degree installed. Filtered water leaves through the outlet pipe (OUT).
REGENERATION
The continuous settling of suspended solids inside the filtering cylinder (1) obstructs the passage of water which results in a pressure difference (∆P). At a preset value of ∆P (range 0.3 ÷ 1 Bar) an automatic cycle will start to clean the filter cylinder (1), this operation begins with a signal that opens the discharge valve (2) and creates communication between the suction nozzles (3) with the outside environment. At the same time, the electric motor (4) creates a rotating motion which enables the nozzles to inspect the filtering surface. Dirt is ejected through the discharge valve (2). The cleaning cycle lasts approximately 15 seconds. The cleaning cycle lasts approximately 15 seconds.
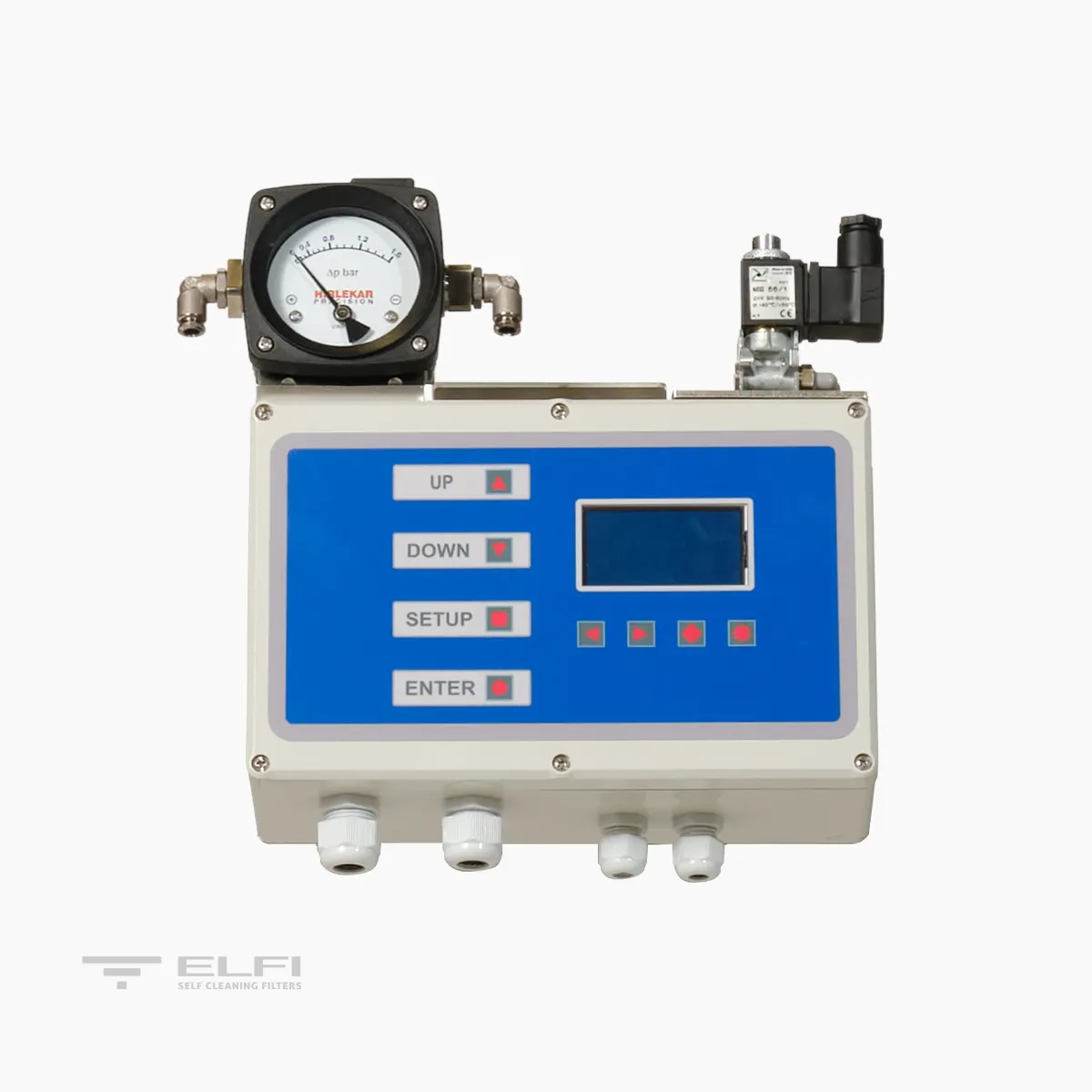
CONTROL
A switchboard controls the washing phases. The signal that starts the cleaning cycle is given by a differential pressure switch. The switchboard gives an “alarm” signal in case of problems in the washing system. These signals can be sent to a pre-existing control center. The washing phase can also be controlled manually. The solenoid controlling the valve is pneumatic.
3D FILTERING TECHNOLOGY
The filtering element of the filtering fabric is made of AISI316 sintered fibre. This ensures high permeability with excellent filtering efficiency owed to the fabric’s thickness (hence called 3D) and the diameter of the fibres. At equal surface and pressure differential, this type of construction allows retention of a much greater amount of TSS (Total Suspended Solids) compared with traditional single thread fabrics. Additionally, exposed to Delta P, the fibres are far more stable compared with single thread fabrics. The filtering fabrics used are tested in our laboratories to assess the performance of the main filtering process.
Based on performance assessments, the most suitable fabrics for the requested use are selected.
SELF CLEANING FILTER MSCR – PP MICRON
Technical Specifications
| MSCR PP -1″1/2 – 7 | MSCR PP -1″1/2 – 15 | |
|---|---|---|
| Filtration area (cm²) | 700 | 1450 |
| Flow rate max – m³/h (ΔP 0,2 Bar) | 10 | 15 |
| Connection In/Out | 1″1/2F | 1″1/2F |
| Discharge | 1″ F | 1″ F |
| 1 Bar washing flow rate with mesh 125 micron – m³/h | 2 | 5 |
| Wash duration – Sec. | 15 | 15 |
| Pressure min-max – Bar | 1-6 | 1-6 |
| Temperature max – °C | 40 | 40 |
| Power supply – Volt | 230 50/60Hz | 230 50/60Hz |
| Power required – Watt | 90 | 180 |
| Construction certificates | CE | CE |
| Maximum size of inlet particles* (filtration from 20 to 1 μm) – mm | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| Max total suspended solids at inlet (filtration from 20 to 10 μm) – mg/l | 20 | 20 |
| Max total suspended solids at inlet (filtration from 20 to 10 μm) – mg/l | 10 | 10 |
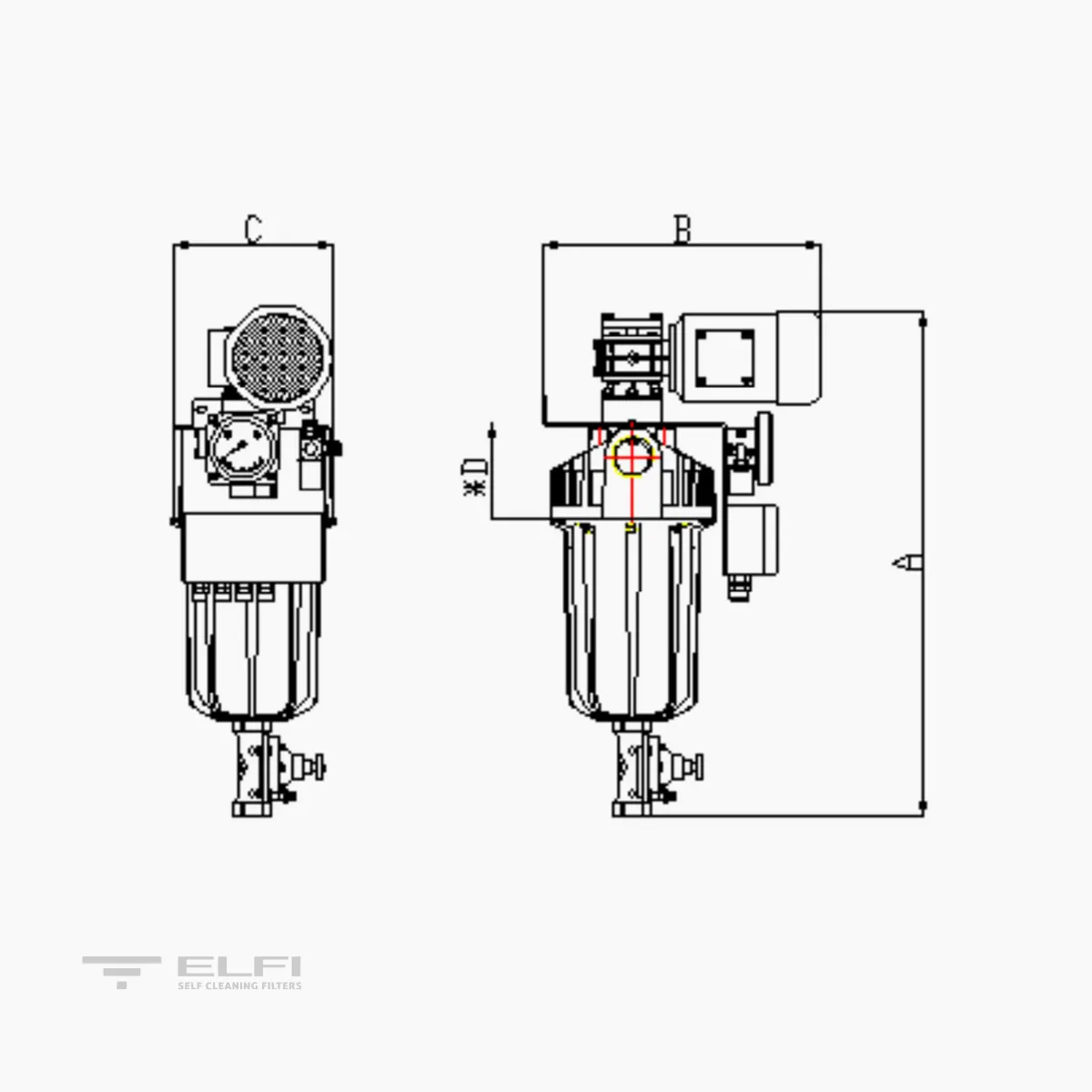
| A (mm) | 610 | 855 |
| B (mm) | 320 | 320 |
| C (mm) | 190 | 190 |
| D* Cartridge extraction (mm) | 250 | 500 |
| WEIGHT Kg | 7 | 12 |
FILTERING MESH FLOW RATE TABLE FOR MSCR FILTERS (m³/h)
| MODEL | 20 µm AISI316 | 15 µm AISI316 | 10 µm AISI316 | 5 µm AISI316 | 1 µm AISI316 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSCR PP MICRON 1″1/2 – 7 | 10 | 9 | 7 | 5 | 2.5 |
| MSCR PP MICRON 1″1/2 – 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 14 | 7.0 |